
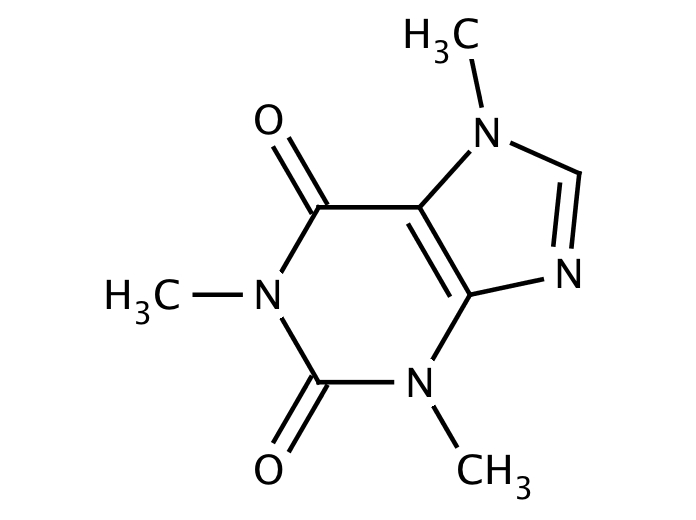
Some "Energy drinks" such as Red Bull contain considerably more caffeine per serving, ranging from 100 to 400 mg. Globally, coffee is consumed as a functional beverage due to its nutraceutical value and positive physiological effects. Caffeine has a chemical structure of C8H10N4O2. Such drinks typically contain about 25 mg to 50 mg of caffeine per serving. The chemical is also known as caffeine, theine, mateine, guaranine, or. Tea contains somewhat less caffeine per serving than coffee, (usually about half as much, depending on the strength of the brew), though certain types of tea, such as Lapsang sou chong smoked teas, and oolong contain less caffeineĬaffeine is also common in soft drinks such as Cola. Caffeine Structure The medical name, derived from its molecular structure, is 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine. Coffee extracted from coffee bean is also present in crimson fruits is completely removed, and the spermoderm is removed, occasionally. This policy directly affects the cache’s hit rate. Introduction Coffee consists of ripe seeds of Coffea arabica Linn., belonging to family Rubiaceae. An eviction policy decides which objects should be deleted at any given time. One fundamental difference between a cache and a Map is that a cache evicts stored items. Another of coffees interesting components are acids. Tea is another common source of caffeine in many cultures. In this article, we’re going to take a look at Caffeine a high-performance caching library for Java. Caffeine is a purine alkaloid, and its chemical composition is C8 H10 N4 O2. In the present work direct determination of caffeine in aqueous solution of green coffee bean was performed using FT-IR-ATR and fluorescence spectrophotometry. In the real world, coffee varies considerably in caffeine content per serving, ranging from about 75 mg to 250 mg. This study was conducted to develop fast and cost effective methods for the determination of caffeine in green coffee beans. In theory, a single serving (6 fl oz / 150 ml) of drip coffee or one-half caffeine tablet would deliver this dose. One dose of caffeine is generally considered to be 100 mg. Caffeine content varies substantially between Arabica and Robusta species and to a lesser degree between varieties of each species. Many of the warning effects of caffeine may be related to the action of methylxanthine on. Caffeine ac-tivates norepinephrine neurons and appears to affect the local release of dopamine. The central nervous system does not seem to develop a great tolerance to the effects of caffeine although dependence and withdrawal symptoms are reported.One common source of caffeine is the coffee plant, the beans from which are used to produce coffee. Caffeine is known to in-crease energetic metabolism throughout the brain, but it also decreases cerebral blood flow, inducing relative cerebral hypoperfusion.

However, children in general do not appear more sensitive to methylxanthine effects than adults. Caffeine exerts obvious effects on anxiety and sleep which vary according to individual sensitivity to the methylxanthine. The effects of caffeine on learning, memory, performance and coordination are rather related to the methylxanthine action on arousal, vigilance and fatigue. Its psychostimulant action on man is, however, often subtle and not very easy to detect. The methylxanthine induces dose-response increases in locomotor activity in animals. Many of the alerting effects of caffeine may be related to the action of the methylxanthine on serotonin neurons. Caffeine, also known as trimethylxanthine, coffeine, theine, mateine, guaranine, and methyltheobromine, is an alkaloid found naturally in. Caffeine activates noradrenaline neurons and seems to affect the local release of dopamine. Caffeine increases energy metabolism throughout the brain but decreases at the same time cerebral blood flow, inducing a relative brain hypoperfusion. Structural,Chemical,Formula,Of,Caffeine,Molecule,With,Roasted,Coffee,Beans. Caffeine is so widely available that the U.S. The only likely mechanism of action of the methylxanthine is the antagonism at the level of adenosine receptors. Many of us rely on a morning cup of coffee or a jolt of caffeine in the afternoon to help us get through the day. Mobilization of intracellular calcium and inhibition of specific phosphodiesterases only occur at high non-physiological concentrations of caffeine. Three main mechanisms of action of caffeine on the central nervous system have been described. Caffeine is the most widely consumed central-nervous-system stimulant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
